The Farm Bill is federal legislation that funds a variety of U.S. food and agriculture policies. It began in 1933 when Congress passed the Agricultural Adjustment Act in response to the Dust Bowl. The Food Security Act of 1985 was the first Farm Bill to include a conservation title, providing financial incentives to agricultural producers through the Conservation Reserve Program (CRP).
Today, the Farm Bill is the largest source of funding for conservation on private lands. The 2018 bill provides $60 billion of projected mandatory spending on conservation over 10 years.
Benefits of the Farm Bill to Washington fish and wildlife
- Protecting and restoring shrubsteppe habitat for sage grouse and mule deer
- Establishing and improving riparian buffers along salmon streams
- Correcting fish passage barriers
- Improving water quality and forest health
- Funding conservation easements to protect wetlands, agricultural lands, and forest lands from development
These conservation efforts can also enhance hunting, fishing, and other recreational access opportunities, particularly on private lands.
Farm Bill Conservation Programs
Farm Bill conservation programs are voluntary and incentive-based, with technical and financial assistance serving as the primary incentives. Farm Bill funding is often an integral part of partnerships that bring together producers, non-governmental organizations, tribes, and local, state, and federal agencies. WDFW has a team of private lands wildlife biologists who can help with Farm Bill-funded wildlife conservation projects on private lands.
The Conservation Title of the Farm Bill contains multiple programs, often grouped into four categories:
- Working Lands Programs
- Conservation Reserve Program
- Easement Programs
- Partnership Programs
Southwest Washington Small Forest Lands Conservation Partnership
WDFW is the lead agency for a Regional Conservation Partnership Program (RCPP) project called the Southwest Washington Small Forest Lands Conservation Partnership. A web app is available to provide information and help forest landowners contact local conservation districts and Department of Natural Resources staff for technical assistance.
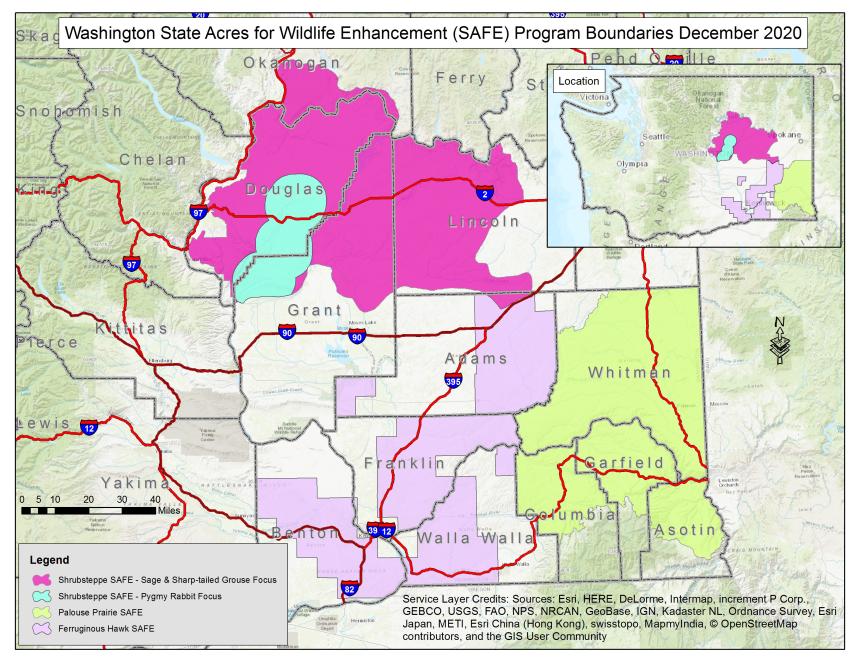
State Acres for Wildlife Enhancement (SAFE)
The State Acres for Wildlife Enhancement (SAFE) initiative of the Conservation Reserve Program is very popular, with producers enrolling more than 115,000 acres into the program. SAFE creates quality habitat for rare and declining species, wildlife of significant social importance (e.g. upland game birds and deer), and species of greatest conservation need.
Washington's SAFE Programs
Importance of Farm Bill to farmers and wildlife
In June 2020, agricultural producers in Douglas County volunteered to speak in a video about the importance of the SAFE initiative to wildlife conservation and their local economy. The video was in the editing process when the Pearl Hill Fire swept through Douglas County in September 2020, which burned more than 223,000 acres and devastated property, livelihoods, and large swathes of wildlife habitat, including significant acreage enrolled in the the program.
The people and nature of Douglas County are resilient and will build back from the fire, though it may take years to fully recover. Federal Farm Bill conservation programs including CRP and SAFE could provide important financial and technical assistance for fire recovery efforts.
Get involved
If you are interested in learning more about conserving wildlife habitat through Farm Bill conservation programs, please contact your local private lands wildlife biologist or your local U.S. Department of Agriculture Service Center.